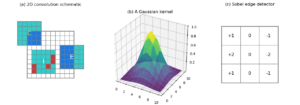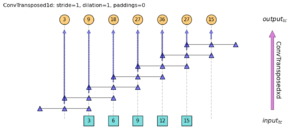


Understanding transposed convolutions in PyTorch
This post explains transposed convolution and relevant module arguments in PyTorch.

A Blog of Programming, Algorithms and Software Tools



A Blog of Programming, Algorithms and Software Tools